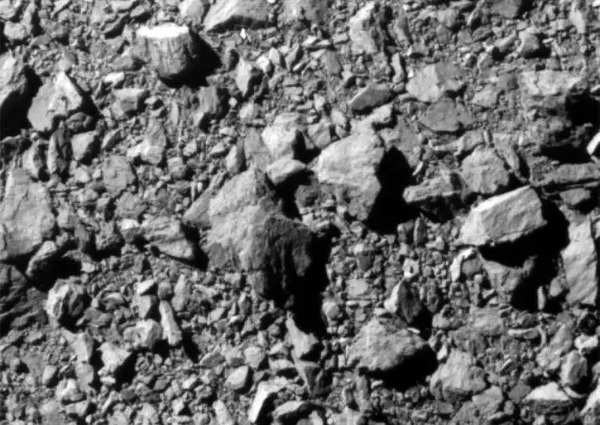
Dimorphos, the smaller companion asteroid, has a floor coated with rocks of assorted sizes, though Dimorphos lacks important cratering, it options a number of cracks or “faults” throughout its floor.
After the groundbreaking planetary protection experiment carried out final yr researchers have analysed information gathered by the mission. The high-resolution pictures have allowed researchers to piece collectively the intricate previous of those two rocky objects, that are located comparatively near Earth.
The photographs have additionally offered invaluable details about how binary asteroid techniques, consisting of a essential asteroid and a smaller moonlet revolving round it, come into existence.
The DART spacecraft captured pictures of the near-Earth asteroids Didymos and Dimorphos earlier than impacting Dimorphos on September 26, 2023. These pictures, together with information from the Gentle Italian Cubesat for Imaging of Asteroids (LICIACube) mission, allowed researchers to review the geological options and bodily properties of the 2 asteroids.
DART, which stands for “Double Asteroid Redirection Check,” solely impacted the smaller physique on this double-asteroid binary system, the moonlet Dimorphos, which orbits the bigger house rock Didymos. Nonetheless, the intention was to see what affect such an influence would have on each our bodies. The info collected throughout this profitable mission may assist scientists higher plan a planetary protection mission to divert an asteroid on a collision course with Earth, House.com reported.
In accordance with Nasa: “These findings give us new insights into the ways in which asteroids can change over time,” mentioned Thomas Statler, lead scientist for Photo voltaic System Small Our bodies at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “That is necessary not only for understanding the near-Earth objects which might be the main focus of planetary protection, but in addition for our potential to learn the historical past of our Photo voltaic System from these remnants of planet formation. That is simply a part of the wealth of latest data we’ve gained from DART.”
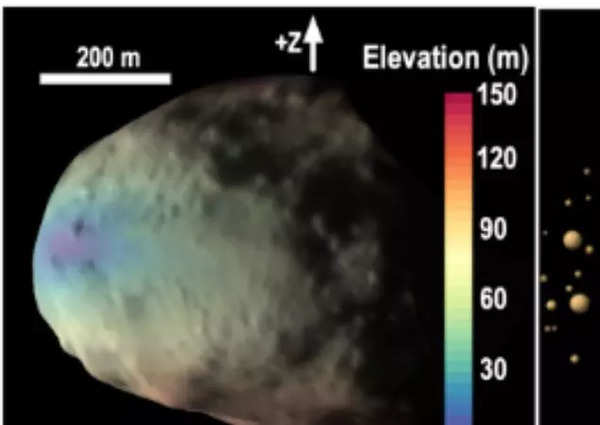
Olivier Barnouin and Ronald-Louis Ballouz from the Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory and his crew targeted on analysing the floor of Didymos, the bigger asteroid.
They found that Didymos has a tough floor at excessive elevations, characterised by massive boulders starting from “33 and 525 toes (10–160 meters) lengthy” and quite a few craters. In distinction, the decrease elevations of Didymos exhibit a smoother floor with fewer massive rocks and craters.
“The photographs and information that DART collected on the Didymos system offered a singular alternative for a close-up geological look of a near-Earth asteroid binary system,” mentioned Barnouin.
“From these pictures alone, we have been capable of infer quite a lot of info on geophysical properties of each Didymos and Dimorphos and increase our understanding on the formation of those two asteroids. We additionally higher perceive why DART was so efficient in transferring Dimorphos,” Barnouin added.
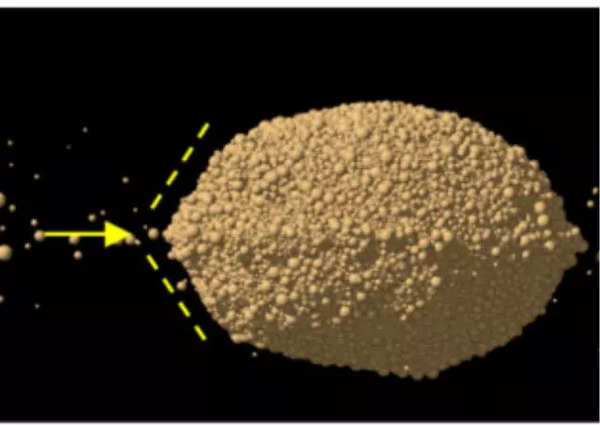
Primarily based on their findings, Barnouin and colleagues concluded that Dimorphos possible shaped from materials ejected from Didymos, which then coalesced underneath the affect of gravity.

The crew employed a technique of counting the craters current on the surfaces of the 2 asteroids to estimate their respective ages. By analyzing the crater information, they concluded that Didymos, the bigger asteroid and father or mother physique, has an age of roughly 12.5 million years.
Dimorphos is considerably youthful, with an estimated age of about 0.3 million years.



